Conditional statements in Java are one of the significant parts of "Control Structure" in Java. Conditional statements are based on certain conditions and generate decisions accordingly. These statements are a bunch of codes that can be executed by "decision statements" which are crucial. In this Java tutorial, we'll learn them in detail. To get into more information, enroll in our Java Programming Course.
Conditional statements are one of the significant parts of "Control Structure" in Java. Conditional statements are based on certain conditions and generate decisions accordingly. These statements are a bunch of codes that can be executed by "decisions statements". These conditions have some specific "boolean expressions." The boolean expression of these conditional statements generates "Boolean Value" which could be either true or false.
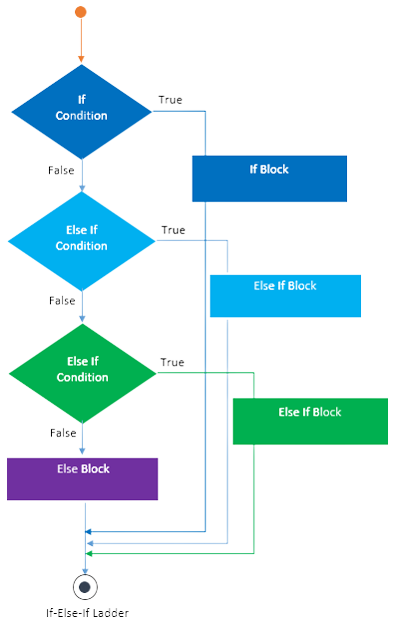
There are 4 types of conditional statements in Java discussed in this Beginner’s Guide to Java. They are if statements in Java, if else statements in Java, ladder statements or If Else If statements, and Switch statements. The types of conditional statements in Java will be discussed further.

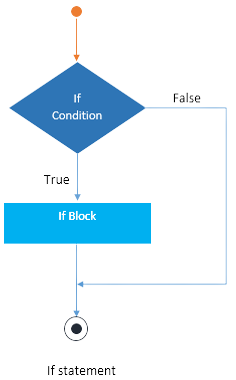
If (condition) < >
if_condition < main < ); > > >
This Java code assigns the value 0.8 to the variable "a," and a "if" condition determines whether "a" is greater than 0. If accurate, it confirms that 0.8 is a positive number by printing "0.8 is a Positive Number!" to the console.
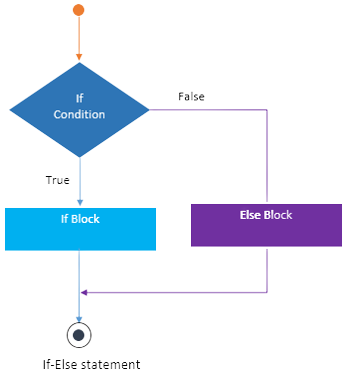
if_else_condition < main < ); > ); > > >
This Java code gives the value -0.8 to the variable "a". It determines whether "a" is greater than 0 by using a "if-else" condition. If true, the console displays "0.8 is a Positive Number!"; if false, it displays "0.8 is a Negative Number!" to indicate that -0.8 is a negative number.
NestedIfElseCondition < main < = = = System.out.println( + perc); System.out.println( <span grade of the student is: "+ grade); > >
With the help of this Java program, you can figure out a student's percentage, give them a grade based on predetermined ranges, and print out both the % and the grade. In this instance, the "nested_if_else_condition" class, which assesses student performance, would output the percentage and grade based on the 382 total marks.
The percentage of the student is: 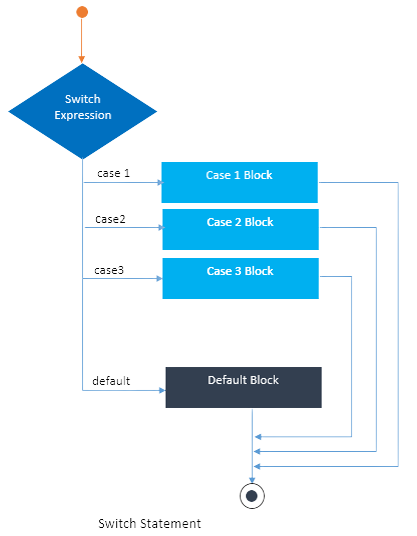
Switch_Case < main < ); ); ); > > >
The switch-case statement is used in this Java code demonstration in the Java Compiler. Because it matches the 'C' case, it examines the value of the character variable "a" and prints "Letter C," but the default case is not used.
Letter CThis article gives a vast idea of conditional statements and their types. Features of every conditional operator in Java with examples and syntax are explained. This article also includes the different types of conditional statements in Java and the difference between the If-else condition and the switch condition.
Java conditional statements are control structures that let you run several code blocks in accordance with predefined conditions.